Connection Broker
Do you already have your own RDSH servers and want to manage them via oneclick™? Read here how you can set up a powerful RDSH farm using a Connection Broker and a Gateway Server.
What is a Connection Broker?
The Connection Broker (CB) manages and mediates connections between users and available resources, such as Remote Desktop Session Hosts (RDSH). It ensures that users are evenly distributed to the required resources (“Round Robin”) by assigning them based on availability, user logins and user policies. A CB can be useful in environments with several RDSHs, as it facilitates administration and scaling.
Connection Broker or oneclick™ Autoscaling - Which one is right for you?
oneclick™ offers modern load balancing including autoscaling, which makes the use of a CB in environments with several RDSHs redundant, offering a more modern load balancing. This means a CB may not be necessary in the server environment. oneclick™ Load Balancing allocates users based on several factors: logged-in users, CPU load and RAM capacity. This ensures that users are assigned to the most appropriate server (in contrast to the simpler Round Robin procedure of a CB). In addition, oneclick™ Autoscaling offers the possibility to create, start and shut down or deallocate RDSH servers as required and thus contributes to the effective and cost-efficient use of IT resources in larger environments. For more information, read our articles on the oneclick™ Load Balancing and Autoscaling technologies.
In oneclick™ an RDSH farm with CB can only be operated using a Gateway Server.
The CB must be connected via VPN IPsec, as it returns the internal host name of the RDS servers. oneclick™ resolves the host name to the internal IP and then connects internally to the RDS servers via VPN.
- The network in which the CB is located must be connected to oneclick™ via VPN and has to be created as a destination as well. To do so, follow our VPN IPsec instructions.
- Then create the Connection Broker as a destination twice and enter the internal IP address here:
- As a destination with port 3389, so that it can be selected as a destination in the settings of the respective app instance.
The internal host name must be entered here during creation! - As a destination with port 443, for its function as a Gateway Server.
The internal host name does not need to be entered here!
- As a destination with port 3389, so that it can be selected as a destination in the settings of the respective app instance.
- The RDS servers to which the CB is to connect must also be created as destinations. Enter the internal IP address here as well.
The internal host name is not required at this point. - Create a destination pool in which you include the RDS servers as well as the Connection Broker (with port 3389).
- If there are several servers in this pool, the CB with port 3389 should be selected as the default destination.
- The Connection Broker with port 443 only serves as a Gateway Server and does not necessarily have to be included in this destination pool.
- Follow the instructions for creating an app configuration for access to an entire desktop.
- In this process, select the pool with the Connection Broker.
- Activate the switch under “Connection settings”.
- The CB with port 443 must be selected as the Gateway Server. If it is not possible to select the Connection Broker with port 443 at this point, check whether it has been created as a destination in advance (see point 2).
- Afterwards, enter the following character string under “Load balance info”:
The “Collection Name” is the name of the RDS collection, for example:
tsv://MS Terminal Services Plugin.1.[collection name]The collection name was defined by the server administrator and can be determined using Powershell.tsv://MS Terminal Services Plugin.1.MySessionCollection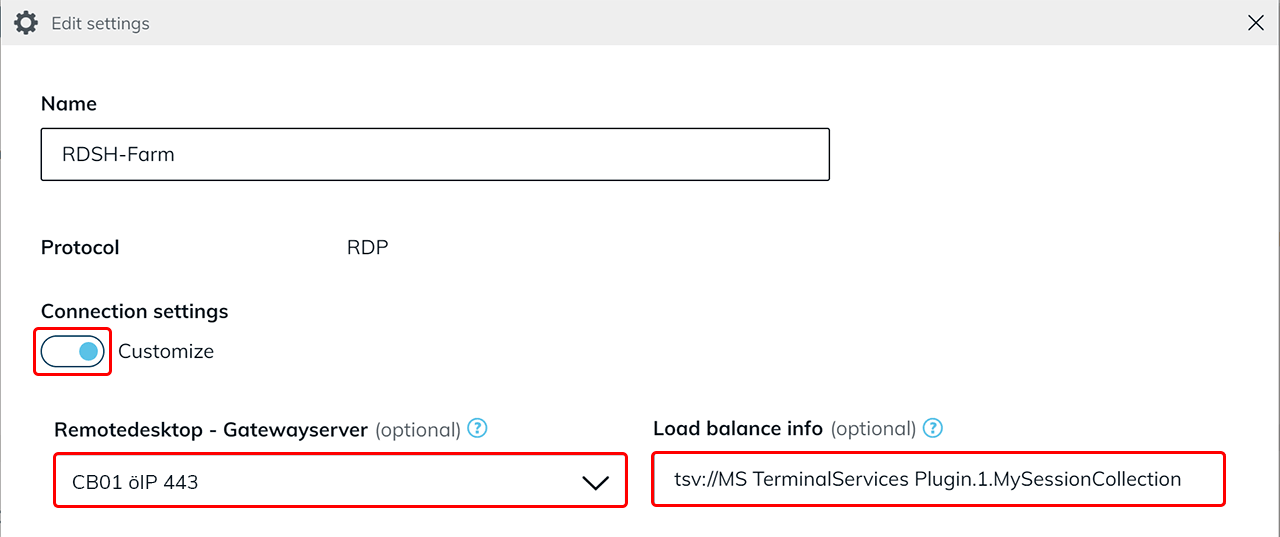
- Create app instances for your users.
- Select the connected CB as the destination, or your default destination if the CB was defined here previously (see point 4).
- Enter the correct access data of the domain user for the CB.