Autoscaling
The cloud providers Ionos and Vultr do not yet support the autoscaling function.
Using the autoscaling function, the system automatically creates and deletes virtual machines as required, based on a base VM provided by you. The system distributes the load dynamically (load balancing), depending on user traffic, CPU load and RAM allocation.
In addition, autoscaling can be used to deploy alternative instance types and thus ensure a smooth process in the event of resource bottlenecks.
If you require local user profiles for your environment, you can solve this using Windows‘ internal board tools (e.g. FSLogix).
You have already activated user licenses for your employees, created a corresponding number of users and added a sufficient amount app licenses? You also created or connected a cloud subscription in oneclick™? Then you can start with the autoscaling setup.
The following steps are necessary to set up autoscaling:
- Create network and domain controller
- Create a base VM/master VM, which performs the domain join and is prepared for processes execution (autoscaling uses the process function in oneclick™)
- Create an event profile in which you make the settings for autoscaling
- Activate and set up load balancing in a destination pool
- Start autoscaling by selecting the event profile
It is mandatory that every user accesses the system via oneclick™ streaming to be recognized.
1. Prepare network and optionally the domain controller
- Create a network.
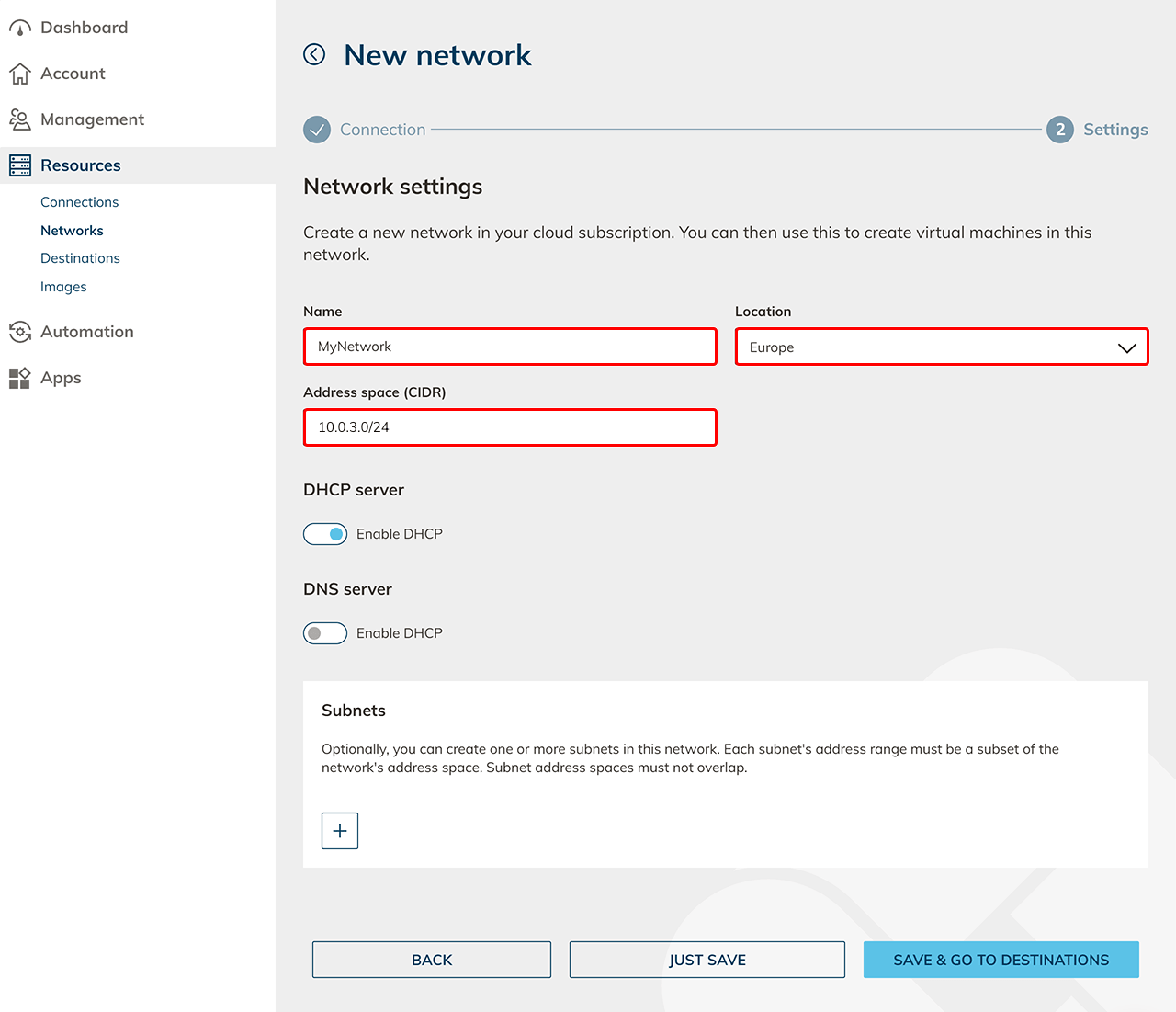
- Create a network security policy for the oneclick™ IP addresses.

- Create a VM, a destination pool, an app configuration and an app instance for your user if you want to use a domain controller for your user administration and their access.
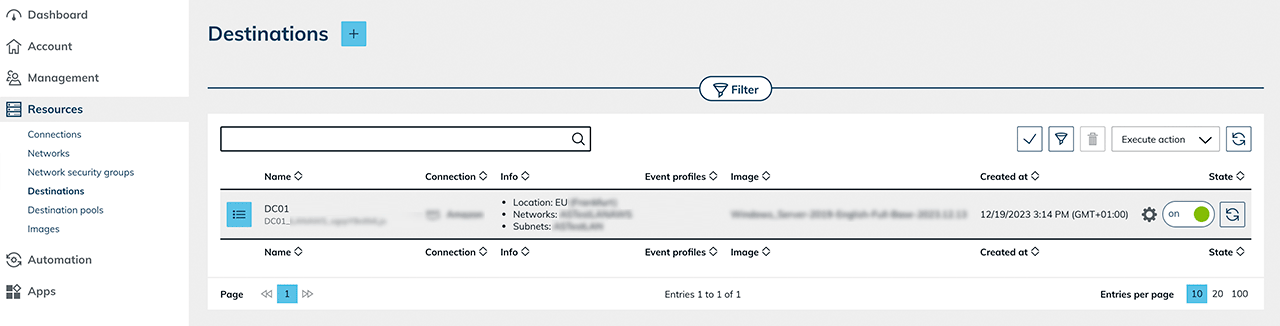
- Then set up this VM as a domain controller.
- If your domain controller is ready for use, edit your existing network security policy. Share the network range of the internal network so that the domain controller and the virtual machines created later can “see” each other.
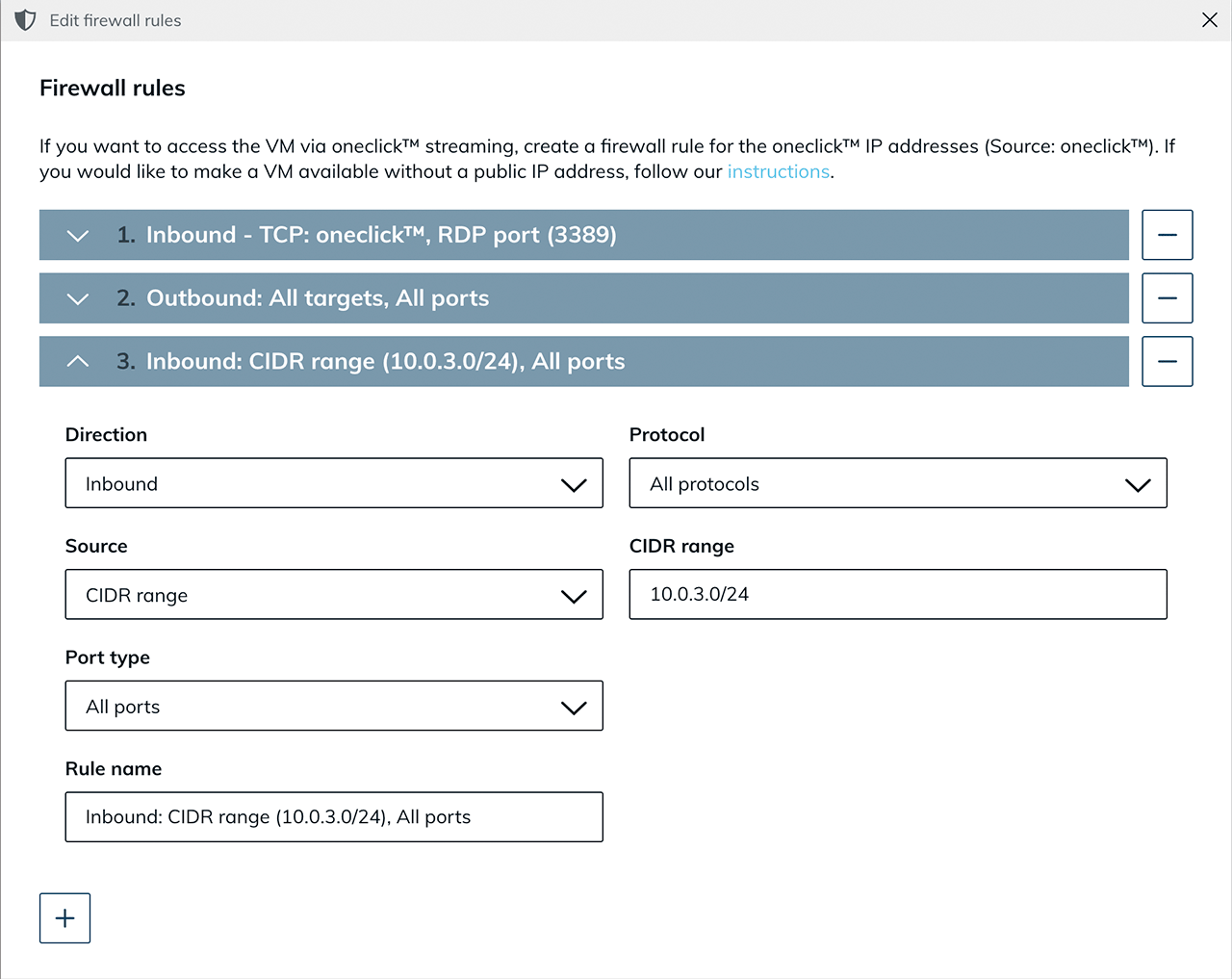
- You can find the CIDR range on the details page of your domain controller.
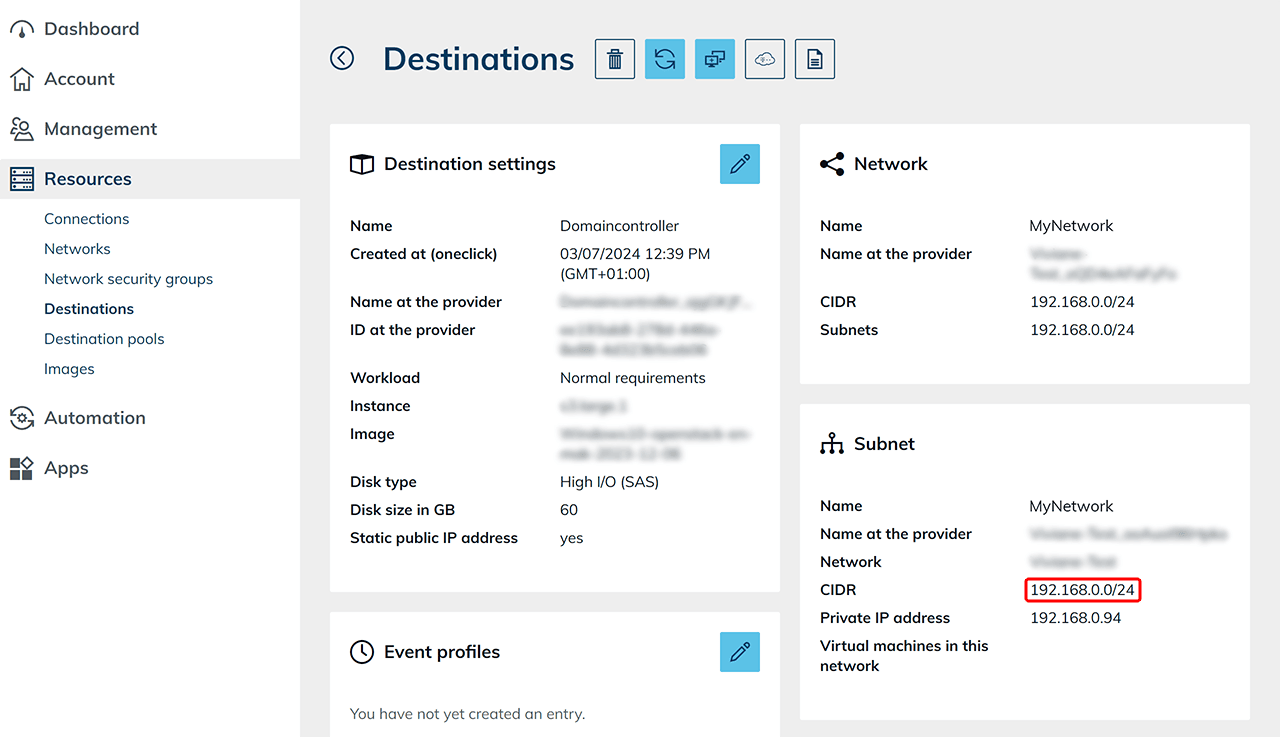
2. Create base VM for autoscaling
Create a VM directly via oneclick™. Proceed as follows:
- Create a VM of the appropriate size, as well as a destination pool, an app configuration and an app instance for your user to access it and set them up. Then create an image. Public images of cloud providers are updated regularly and therefore cannot be used as a base image for autoscaling.
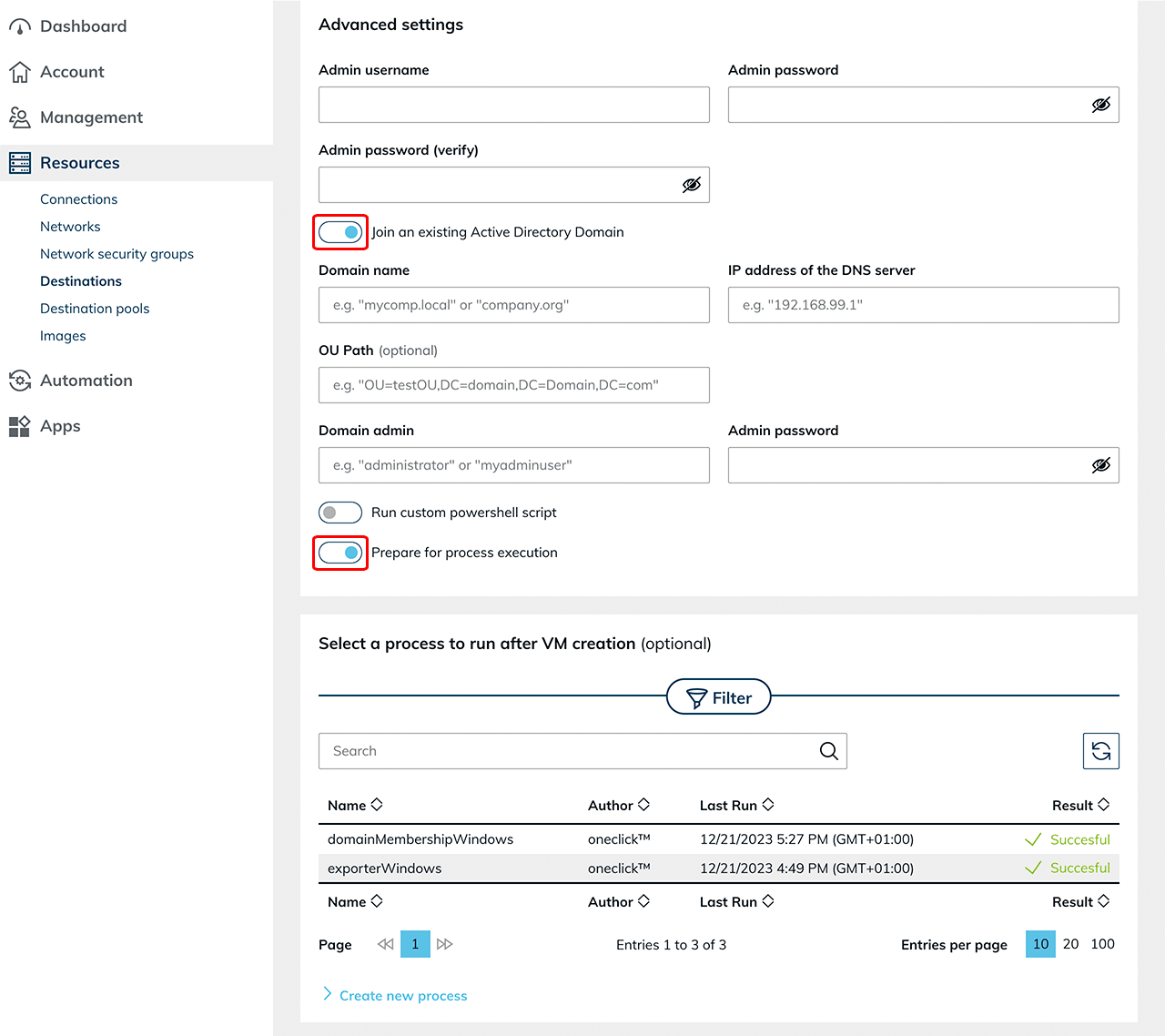
- Then create another VM with the generated image that you want to use as the base VM for autoscaling. In addition to the usual settings (requirement for Windows clients: 4 CPU and 4 GB RAM), select the created image. Activate the switch for "Join an existing Active Directory Domain" and enter the data for a domain join. Leave the switch for "Prepare for process execution" active.
- If you need an RDSH role for the servers, you can optionally run a "Run custom powershell script" process when creating the VM.
 Imported VM from Cloud Subscription: If you want to import the VM that serves as the basis for autoscaling from your cloud subscription, configure it accordingly.
Imported VM from Cloud Subscription: If you want to import the VM that serves as the basis for autoscaling from your cloud subscription, configure it accordingly.
3. Create event profile for autoscaling
-
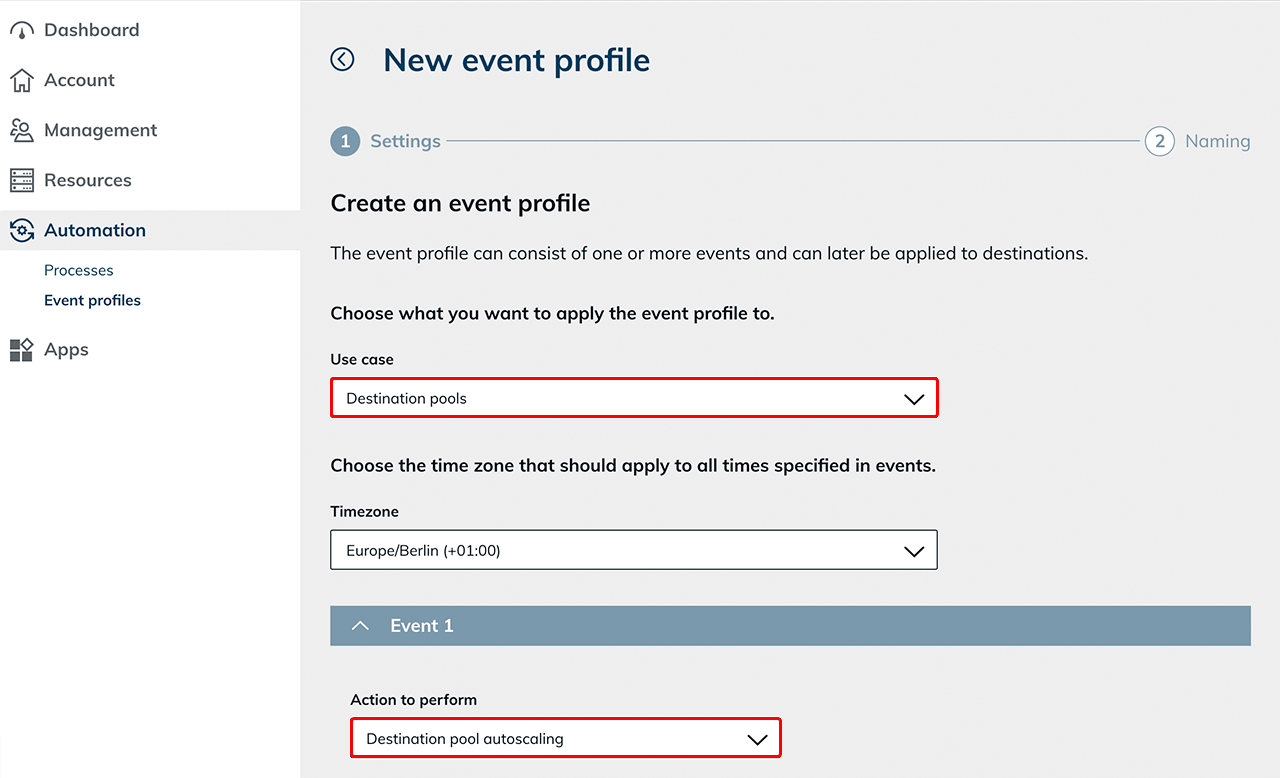
Create an event profile and select the use case for "Destination pools" as well as the right "Timezone".
-
Select "Destination pool autoscaling" as the "Action to perform".
-
Decide on a base VM on which you want to run autoscaling. All VMs used for scaling in the future are clones of this base VM. Depending on the provider, you have the option of using alternative types of instances. This ensures that your VMs continue to run smoothly even in the event of resource bottlenecks by using alternative instance types automatically.
Types of Fallback instances
Activate the switch if you want to set up any types fallback instances. This function is available for the providers Open Telekom Cloud, Orange and Huawei. It enables the use of alternative instance types if the standard instance type is not available in sufficient quantity.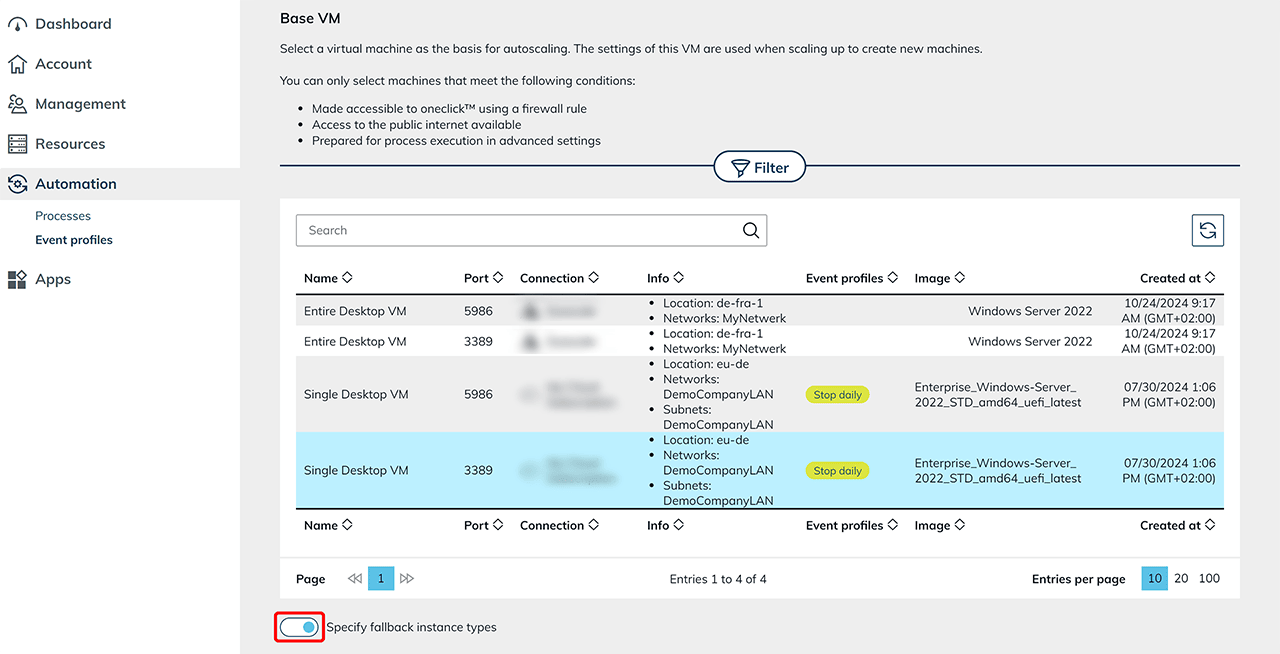 Select the desired fallback instance types from the list of available options.If you want to use fallback instance types only, activate the corresponding option by ticking the box. This ensures that only the fallback instance types are used, even if the original instance type is available. The instance types are used in the order as shown in the list below.
Select the desired fallback instance types from the list of available options.If you want to use fallback instance types only, activate the corresponding option by ticking the box. This ensures that only the fallback instance types are used, even if the original instance type is available. The instance types are used in the order as shown in the list below.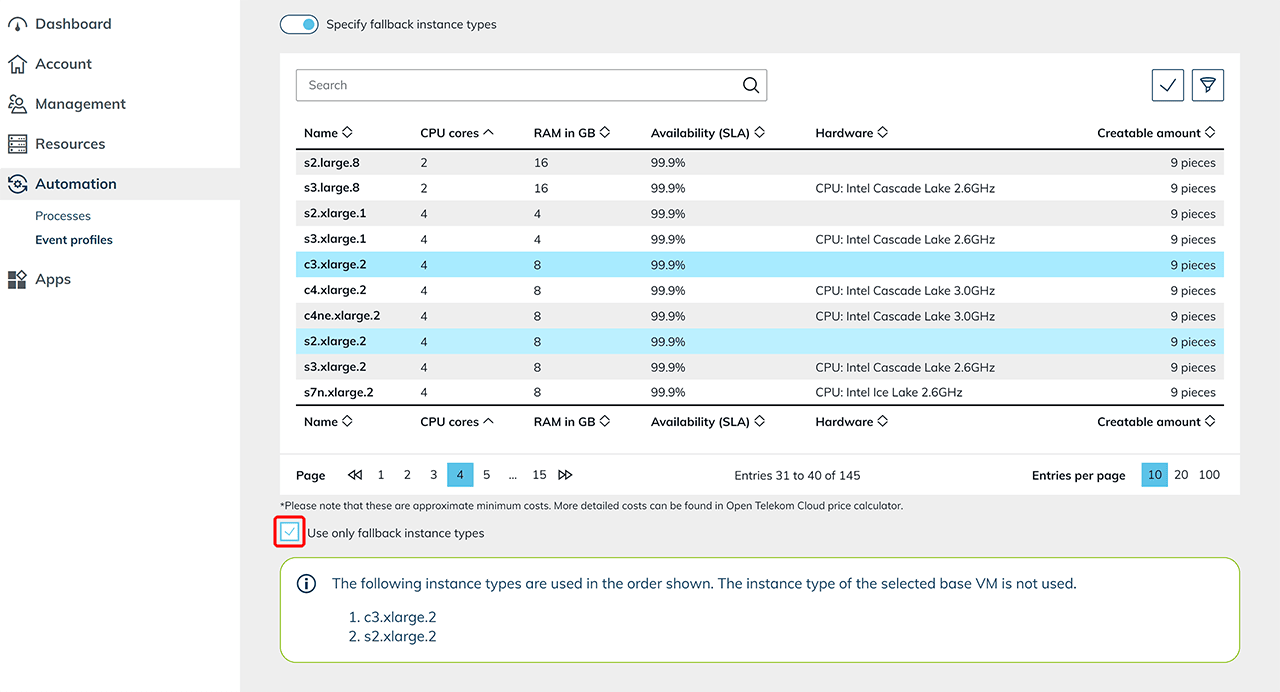
Deviating instance type
For other providers, you have the option of defining a different instance type that is used instead of the basic VM instance type. Activate the switch and select a suitable alternative from the list of supported instance types.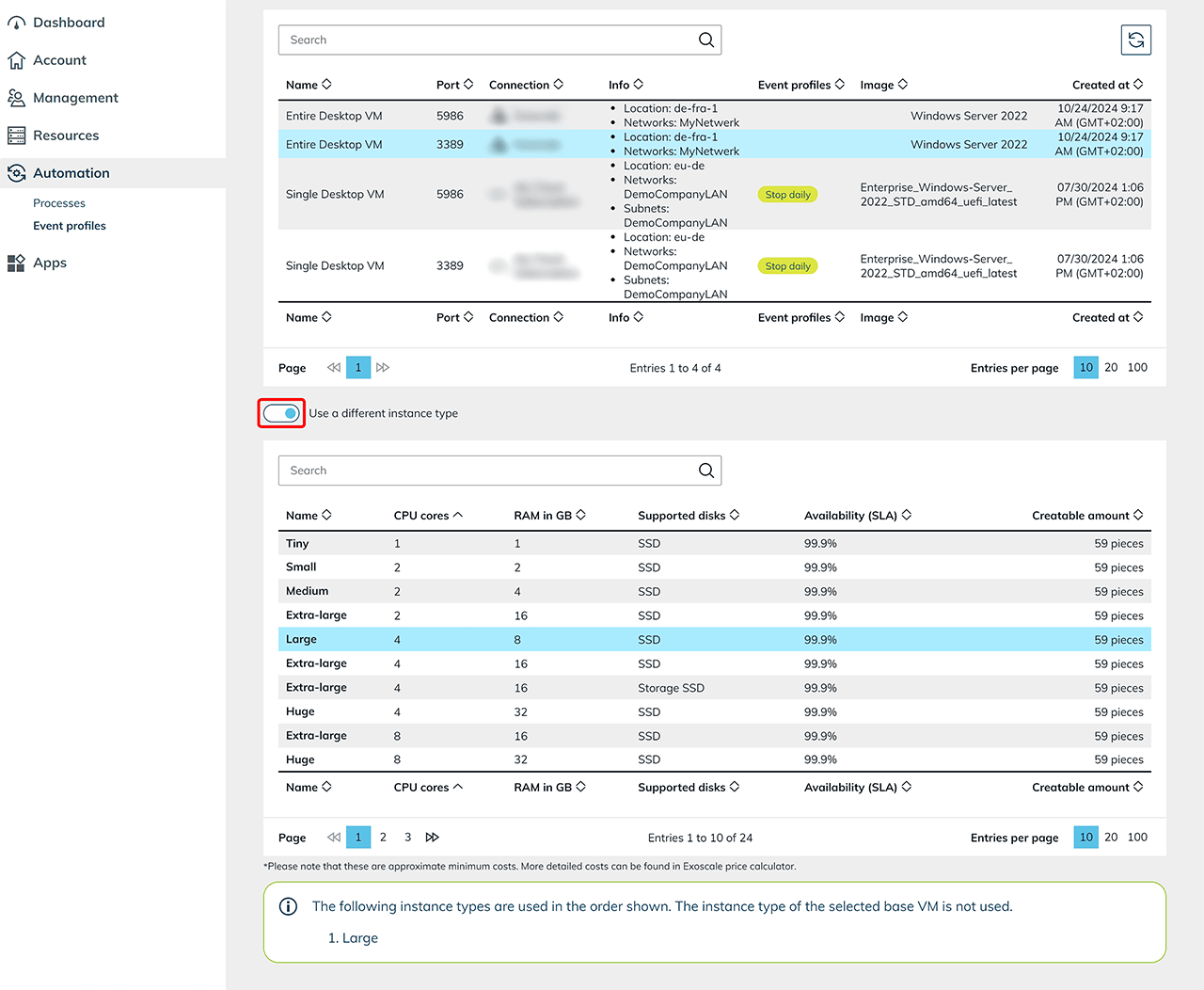
-
Use the slider to select the scaling type. If you are working with programs that require a higher computing power (e.g. CAD programs), single user is the best choice. While working primarily with software that requires less computing power, multi-user is the right choice.

Single user assignment
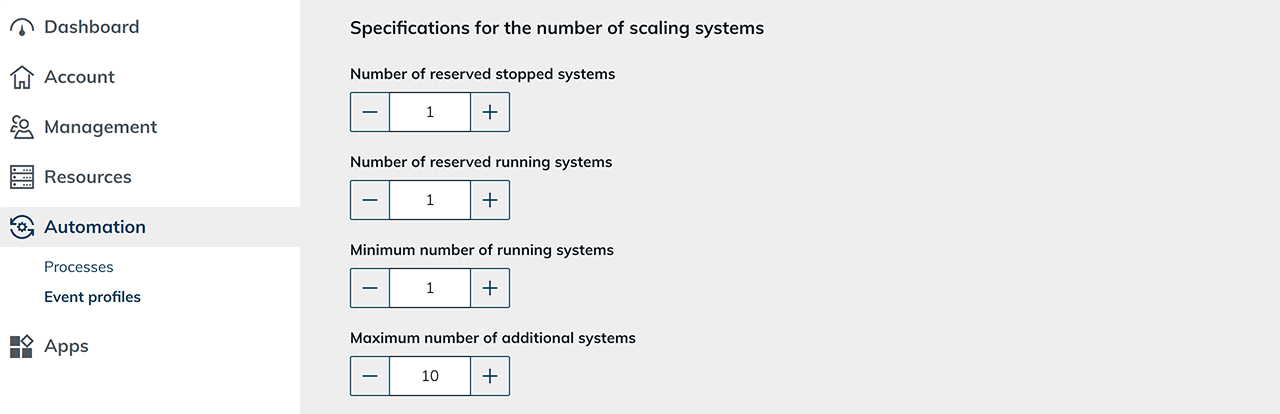
When choosing a single user assignment, define the specifications for the number of scaling systems: Please also note the information regarding scaling up and scaling down that is displayed in the oneclick™ Admin!
- Number of reserved stopped systems: Here you specify how many fully set up systems are to be kept in a stopped state. If one of these systems is in use, oneclick™ automatically creates a new clone and keeps it in a stopped state to restore the number you set in advance.
- Number of reserved running systems: Here you specify how many already running (active) systems are to be kept permanently. Running systems offer particularly fast access to any user interface and are ready for login at any time. Here too, the system automatically creates a new clone as soon as one of the running systems is in use. In the case of single occupancy, at least one system should always be kept running so that a login can take place without delay. If there are several employees, we recommend adjusting the number accordingly to avoid waiting times.
- Minimum number of running systems: Here you specify the minimum number of running systems. This allows you to ensure that there are always enough active systems for your employees ready for login.
- Maximum number of additional systems: Here you specify the maximum number of additional systems. This limit allows you to use resources and funds sustainably.
 The load balancing, as well as active event profiles, will be displayed in the settings of destination pool.
The load balancing, as well as active event profiles, will be displayed in the settings of destination pool.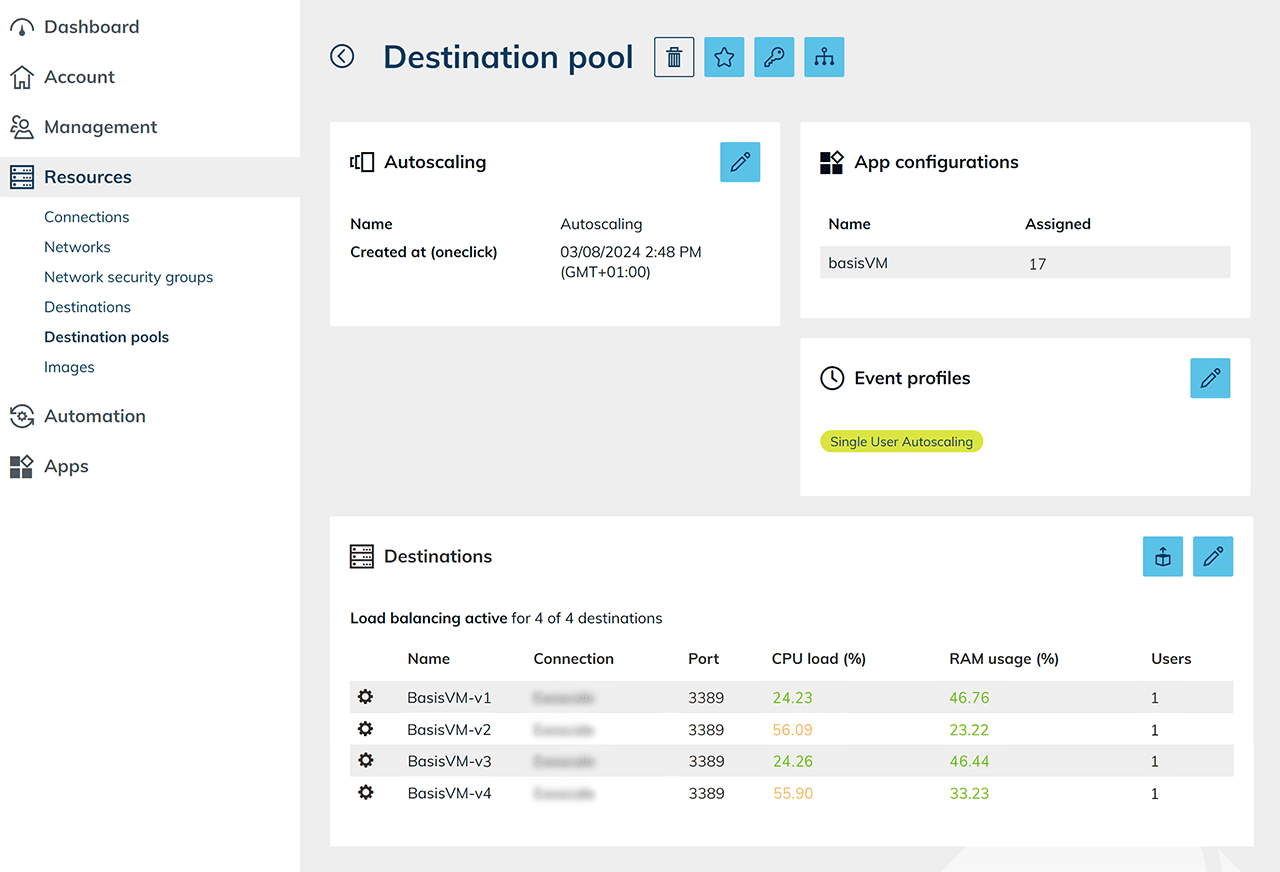 Afterwards, set the interval for the execution.
Afterwards, set the interval for the execution.
Multi user assignment
If you choose a multi user assignment, adjust the settings to your requirements as follows. Please also note the information regarding scaling up and scaling down that is displayed in the oneclick™ Admin!
-
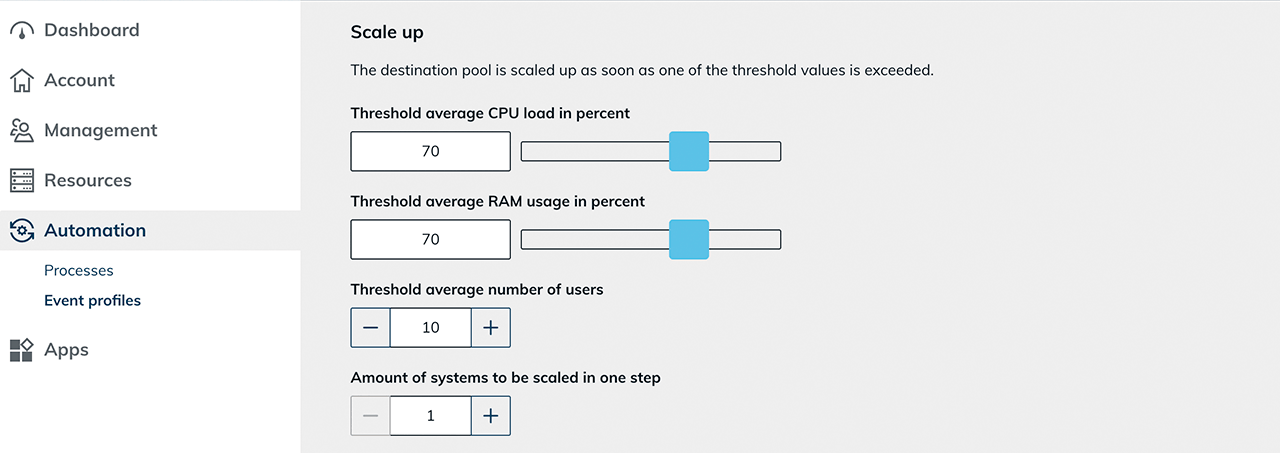
Set the correct limit value for the average CPU load and RAM usage. This is calculated the way you have defined it in the pool in the load balancing settings.
-
Select a limit for the average number of users. If this value is exceeded across all servers, the system scales up. In this case, the system will create additional VMs.
-
Specify the number of systems to be scaled in one step. If the value 1 is set here, for example, exactly one VM is always created before the system is responding to the new conditions.
 In addition, configure the settings to which you want the system to downscale:
In addition, configure the settings to which you want the system to downscale:- Select a limit for the average CPU load and RAM usage.
- Set a limit for the average number of users. When this limit is reached, the system will scale down.
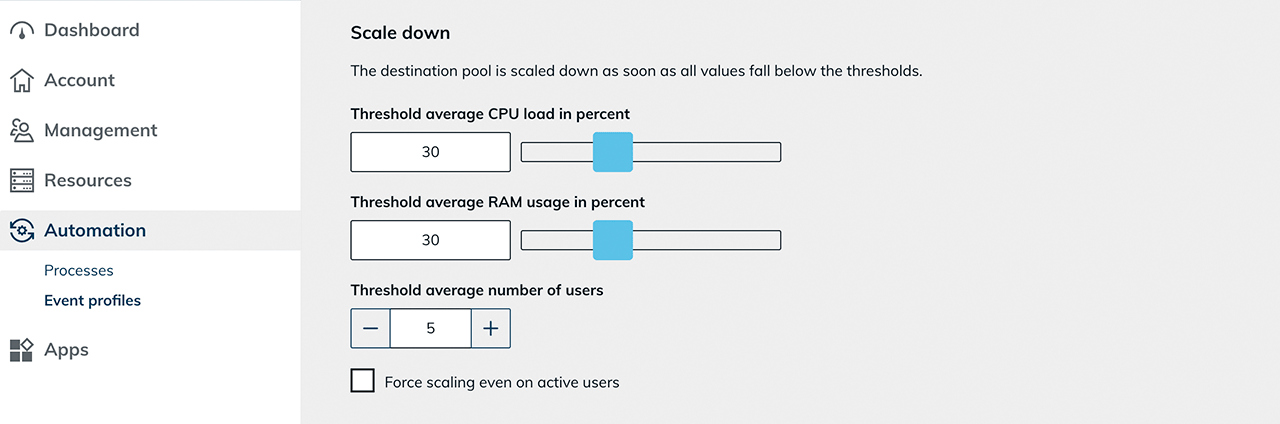
-
Optionally, you can force scaling down even if the users are still logged in. To do so, check the box next to "Force scaling even on active users". Then select the appropriate value for "Time period in minutes before scaling down even with active users". Active users will now be shown a pop-up with the remaining time at the start of the set period.
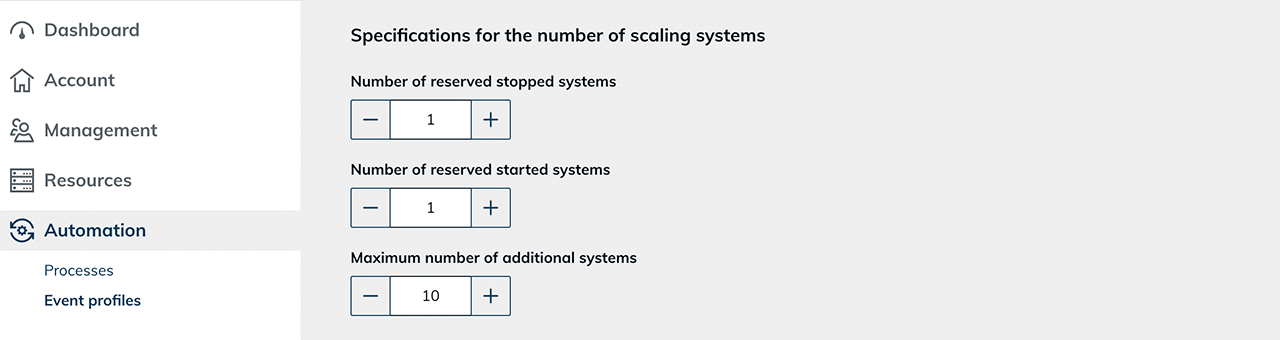
Determine the number of scaling systems:
- Number of reserved stopped systems: Here you specify how many fully set up systems are to be kept in a stopped state. If one of these systems is in use, oneclick™ automatically creates a new clone and keeps it in a stopped state to restore the number you have set.
- Number of reserved started systems: Here you specify how many already running (active) systems are to be kept permanently. Running systems offer particularly fast access to the user interface and are ready for use at any time. Here too, the system automatically creates a new clone as soon as one of the running systems is in use.
It is recommended to always keep at least one system running so that a login can take place without delay. If there are several employees, the number should be adjusted accordingly to avoid waiting times. - Maximum number of additional systems: Here you specify the maximum number of additional systems. This limit allows you to use resources and funds sparingly.
 The load balancing, as well as active event profiles, will be displayed in the settings of destination pool.
The load balancing, as well as active event profiles, will be displayed in the settings of destination pool.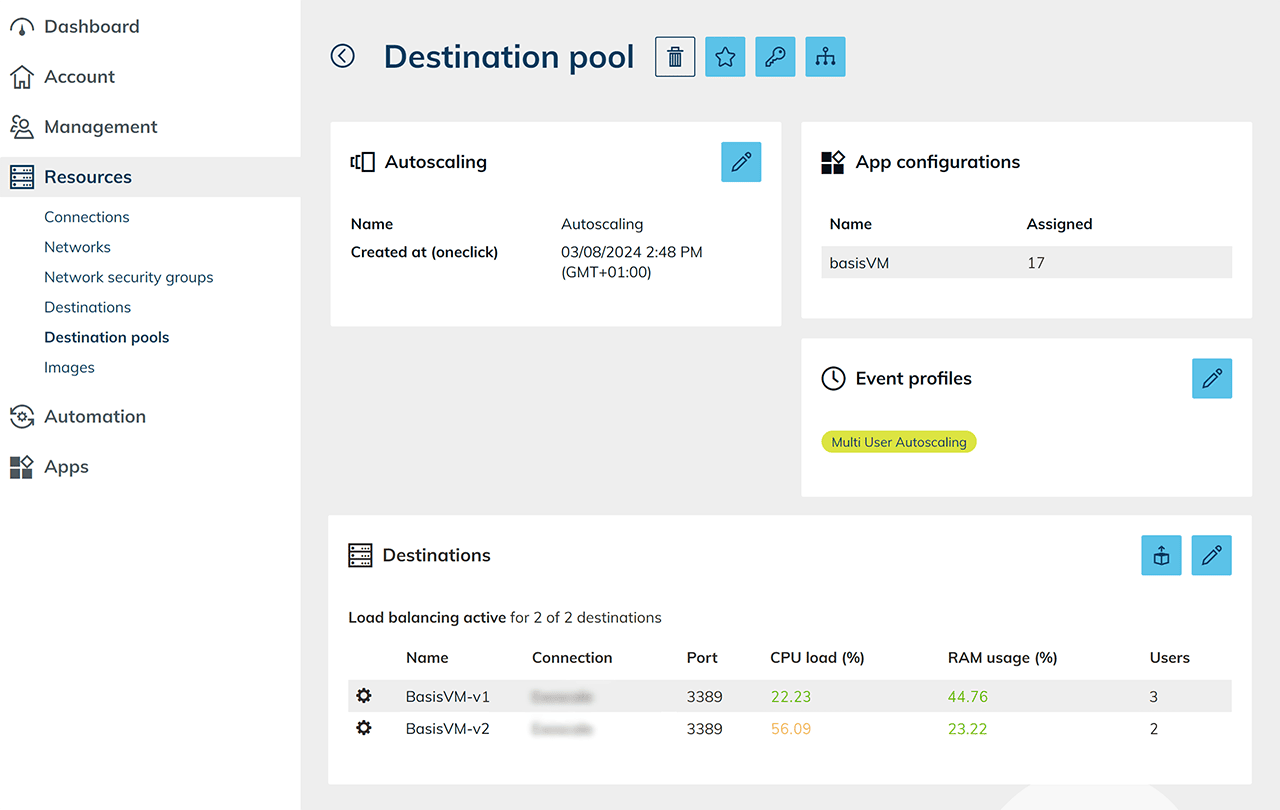
Set interval for execution
Finally, under "Set an interval for execution", specify a starting time at which the settings are to be set.
- For example, if you want your settings to apply from monday to friday, select monday in the calendar menu, as well as the correct starting time and check the "Monday" box.
- Create another event by clicking on the + Icon.
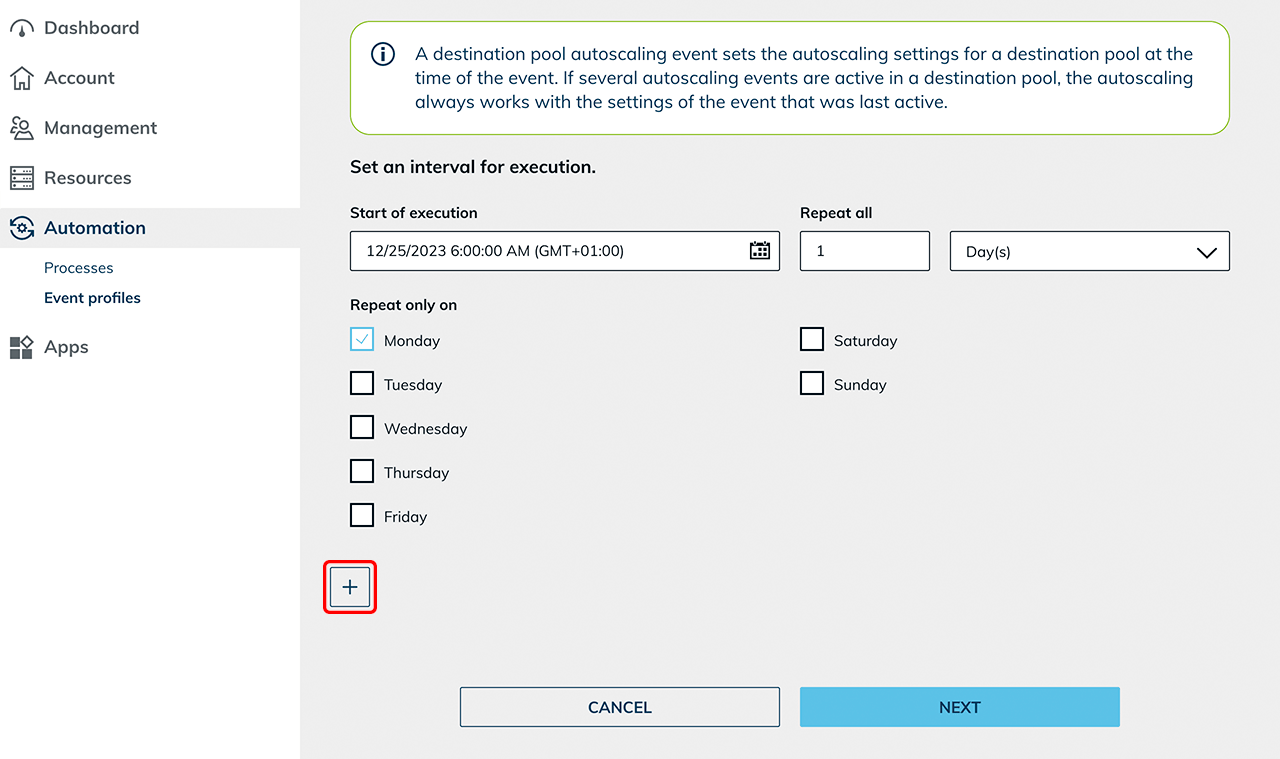
- Now make the settings for the weekend and select friday as the starting time in the calendar menu, as well as a time in the evening from which the settings for the weekend should take effect. Also select „Friday“ as the day of the week in the list below. At this point, the event overwrites the previous settings until the monday event takes effect again.
Find out when your users usually work in order to create the most efficient profile possible. We recommend testing the settings you made with a few users until you have determined the appropriate number of VMs to keep on hold.
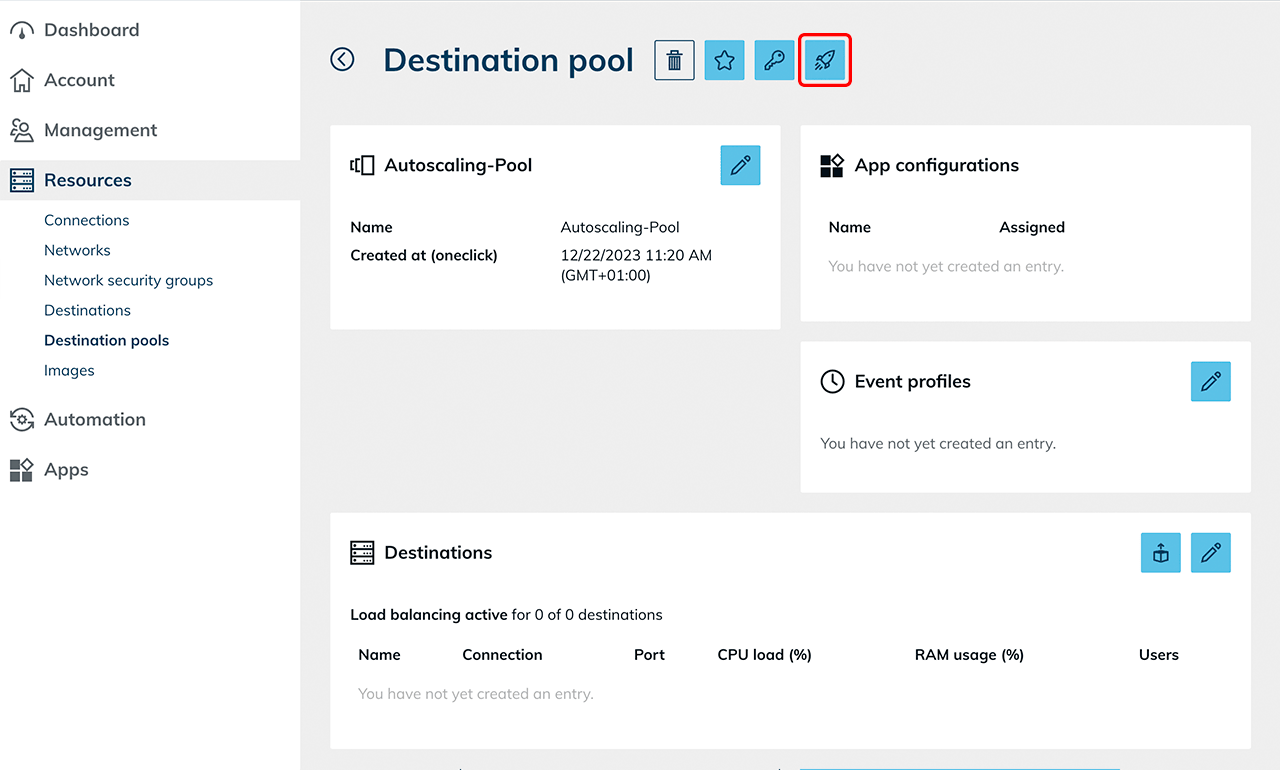
4. Create destination pool and set load balancing
-
Create a destination pool without selecting a destination and activate load balancing for this pool.
-
As the VM was created via oneclick™, the instructions given for preparing load balancing are no longer applicable. All the necessary settings have already been made in advance by preparing the process and selecting the correct network security group.
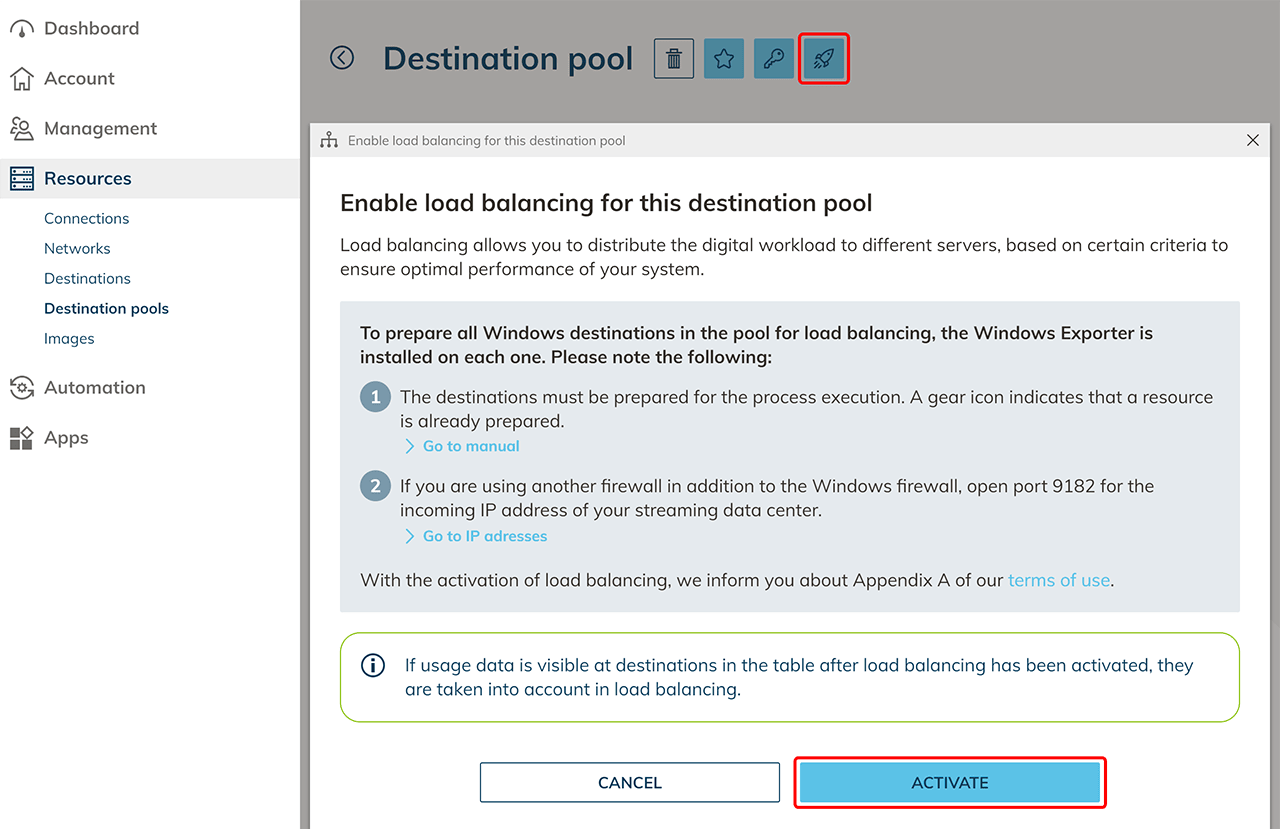
-
Then the function of the button changes and you can make settings for the load balancing.
Single user
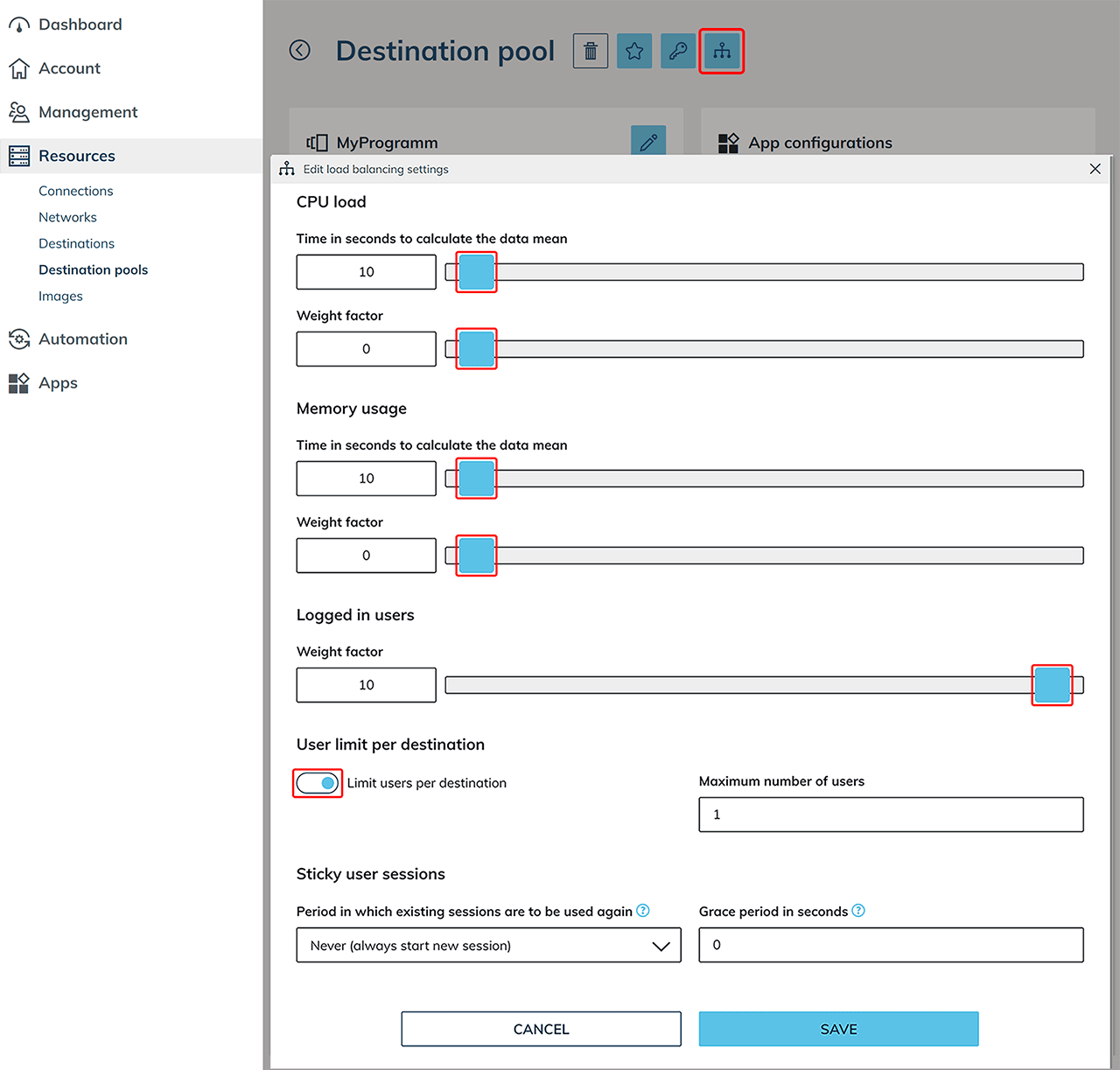
Click on the Distributor symbol and make the following settings for your application with single user VMs:
- Set the weighting factors for "CPU load" and "Memory usage" to 0, as these are not required for the application with single user VMs.
- Set the weight factor for "Logged in users" to 10.
- Activate the setting "User limit per destination" and set the "Maximum number of users" to 1.
- When using a single user VM, make the appropriate settings and set the maximum weight factor for "Logged in users" to 10. Activate the setting "User limit per destination " and determine the "Maximum number of users" to 1.
- The option "Sticky Sessions" is not possible for a single user assignment. Any entries made here will be ignored by the system.
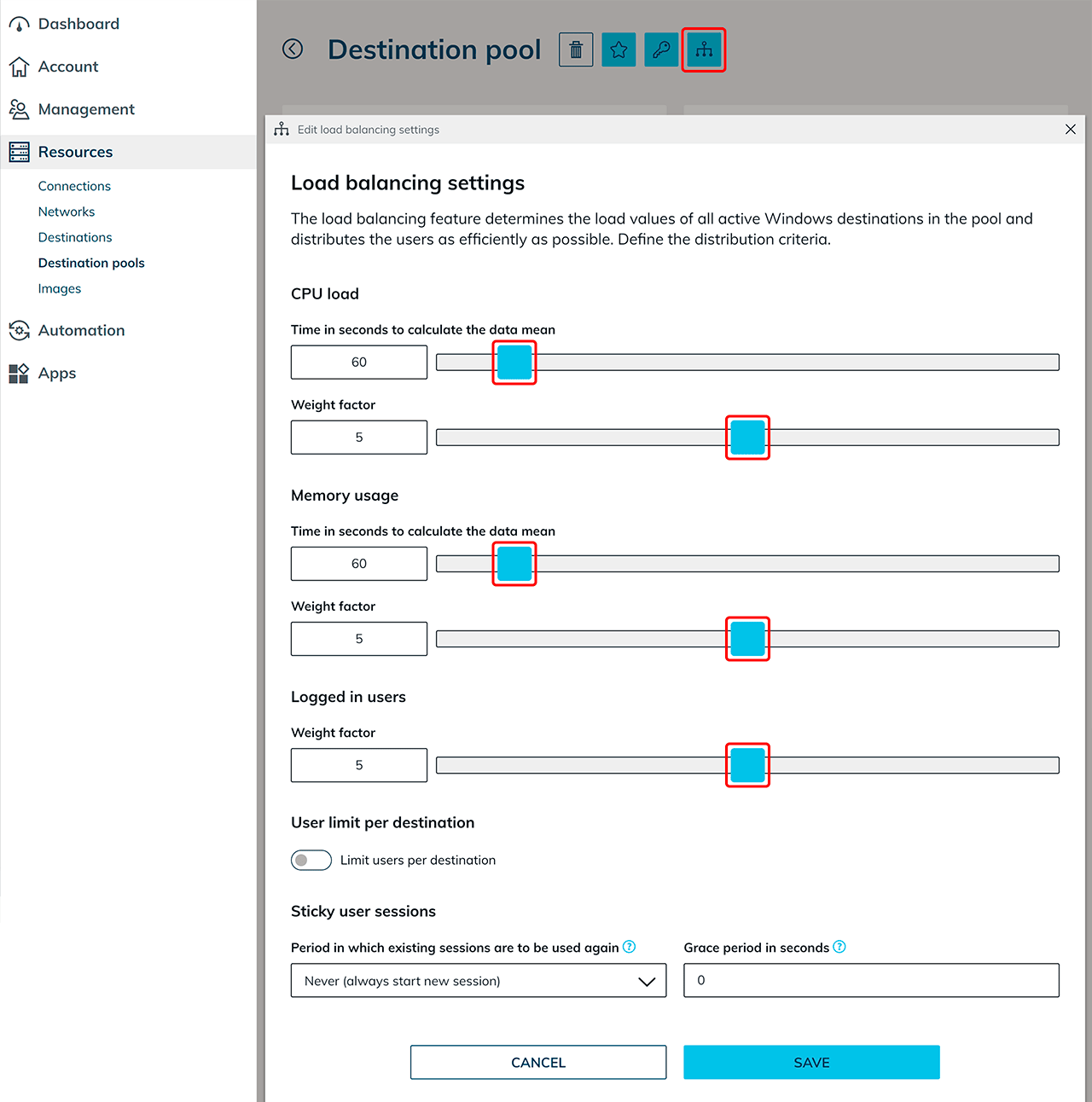
Multi user Click on the Distributor symbol and make the following settings for your application with multi user VMs:
- Change the time for calculating the data average as well as the weighting factor for the CPU load and the memory ossupation. You can also set a value for the weighting of logged-in users. The weighting factor describes the priority the corresponding option should be treated with. The scale ranges from 0 to 10. If several entries receive the same value, they will be treated with the same priority.
- Optionally, you can set a user limit per destination to ensure that no more than X users are allowed on a destination.
- If you would like to use sticky sessions please note our instructions for using sticky sessions.
-
Now create user names and passwords for all your users on your domain controller.
-
Create an app configuration for your pool.
-
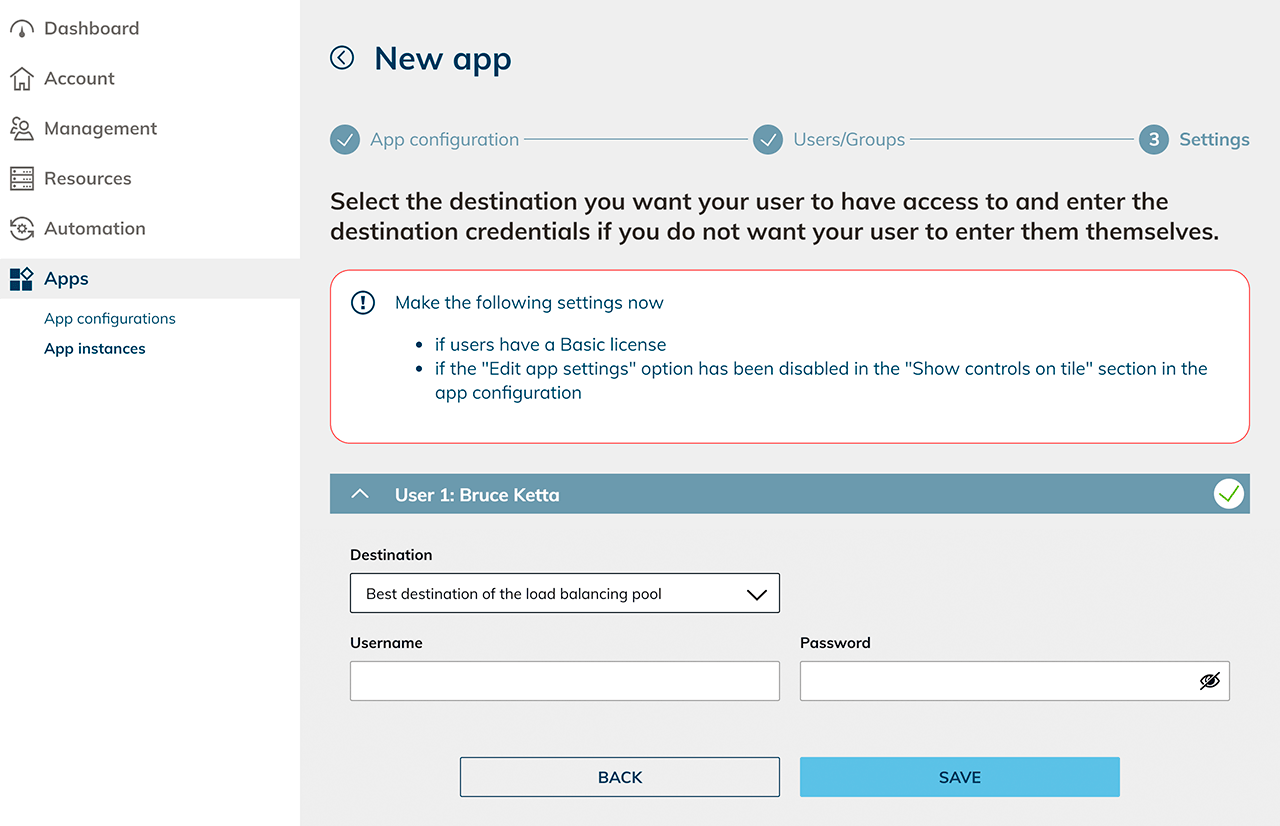
Create app instances with this app configuration. Select "Best destination of the load balancing pool" as the destination and enter the credentials for your users.
5. Start autoscaling
- After finishing all the preparations you can now start autoscaling: Select the autoscaling event profile in your pool.
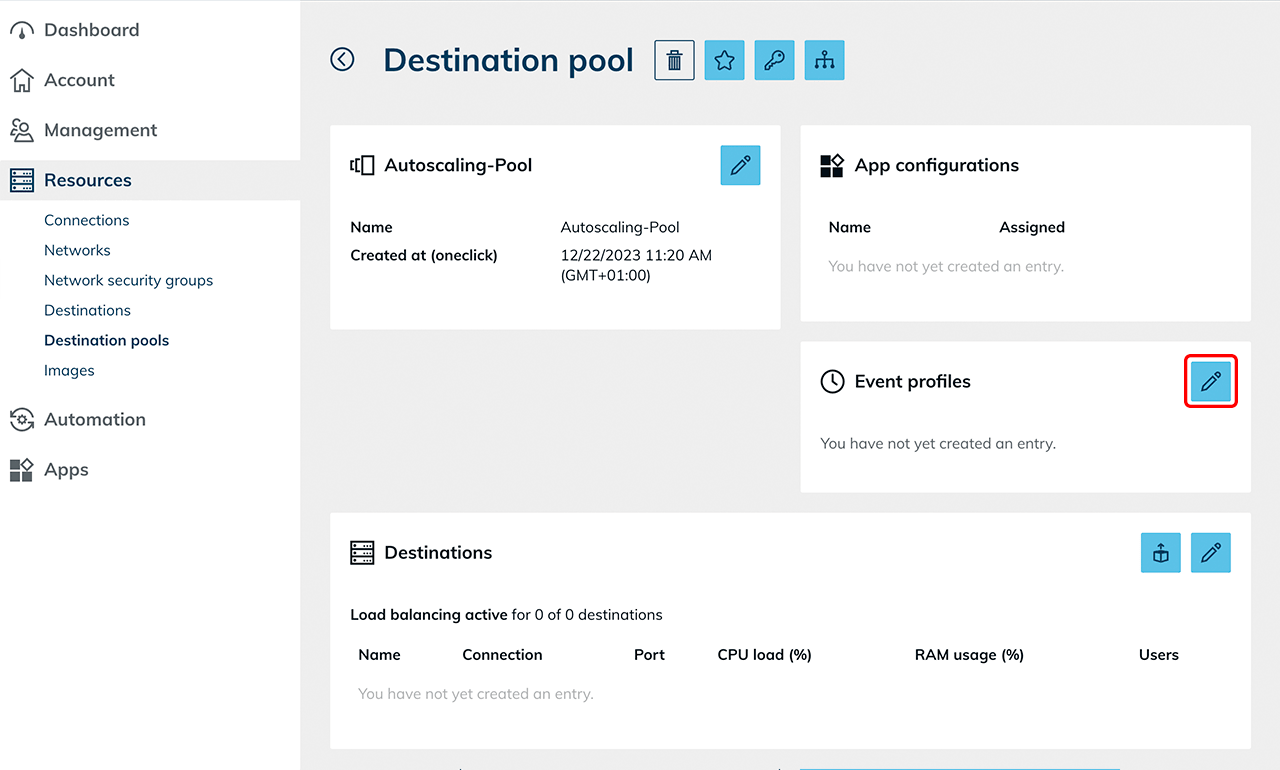
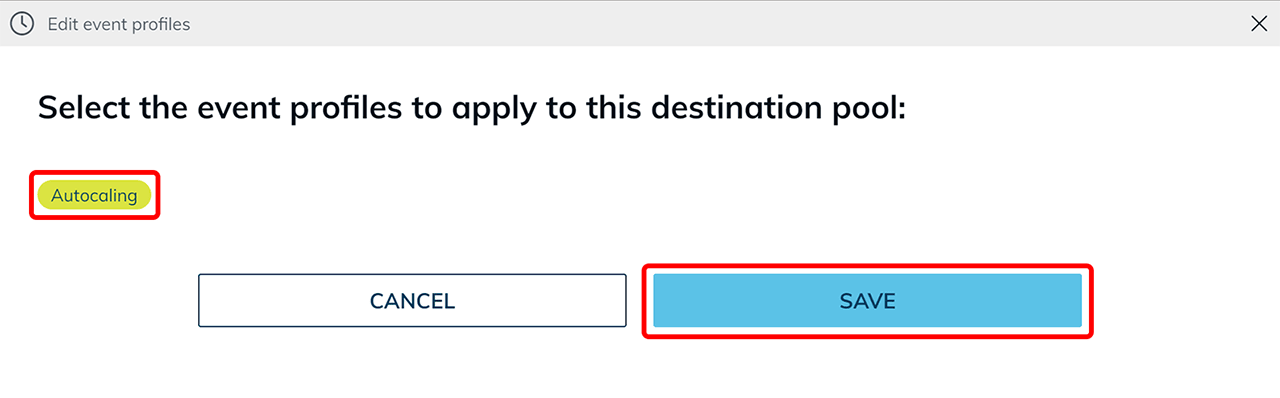
- The following processes are now running:
- Depending on the settings (e.g. one stopped VM and one started VM are to be reserved), two clone VMs are created and the domain join is performed.
- An attempt is made to install the WinRM role on both VMs in order to be able to read the Windows metrics (CPU, RAM, user). In the Processes menu, check whether the process is running successfully or if the role hase been installed correctly. Depending on the system requirements, this process can be triggered several times if the VM does not respond yet.
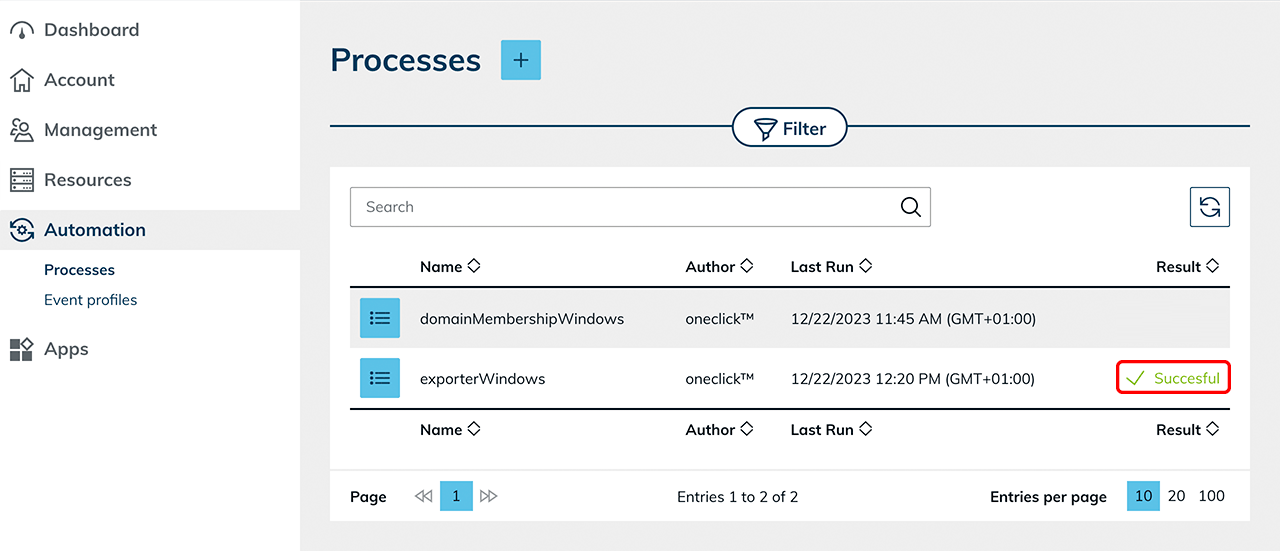
- If, for example, 1 VM is to be kept "off" in the settings, one VM is switched off as soon as the WinRM role is installed.
 The other VM remains "on" and ready so that a user can log in without waiting.
The other VM remains "on" and ready so that a user can log in without waiting.
- As soon as a user logs in, the system will scale up. In this way, the system attempts to return to the initial state, in which a stopped VM as well as a free started VM are kept on hold in addition to the VM in use.
- If the user logs off again or if fewer users are logged in to the VMs on average, the system scales down according to the specified settings. The "domainMembershipWindows" process is executed for the scaled-down VM (the VM leaves the domain) and then deleted so that no further costs can be incurred.
6. Notes on the behavior of autoscaling
In addition to the settings, you also have the option of influencing autoscaling manually.
- You can delete a VM manually if it is damaged. In this case, autoscaling compensates for the lost VM and creates a new one.
- Autoscaling runs once a minute. If the metrics are changing in such a way that scaling is required, it will take at least one minute for the system to react accordingly.
- If no metrics are received from the VM even after several attempts, the system continues to scale up (a new VM is created). The damaged VM will then be deleted after approx. 30 minutes.
- To interrupt autoscaling completely, remove the event profile from the destination pool. This will delete all VMs.
- If a user wants to work independently from autoscaling, to run calculations overnight for example, you can clone your base VM manually and add it to the pool. Then assign your manually added VM to this user through the app instance. All manually added VMs will not be taken into account during autoscaling.
7. Instruction for using Sticky Sessions (in a multi user environment)
By default, the user always receives a new session. However, in oneclick™ you have the option of retaining the session for a specified period of time. To do this, open the drop-down menu under the item “Period in which existing sessions are to be used again” to change it. The time period specified here must then also be set exactly in Windows. (See “Configure Sticky Sessions in Windows” below). 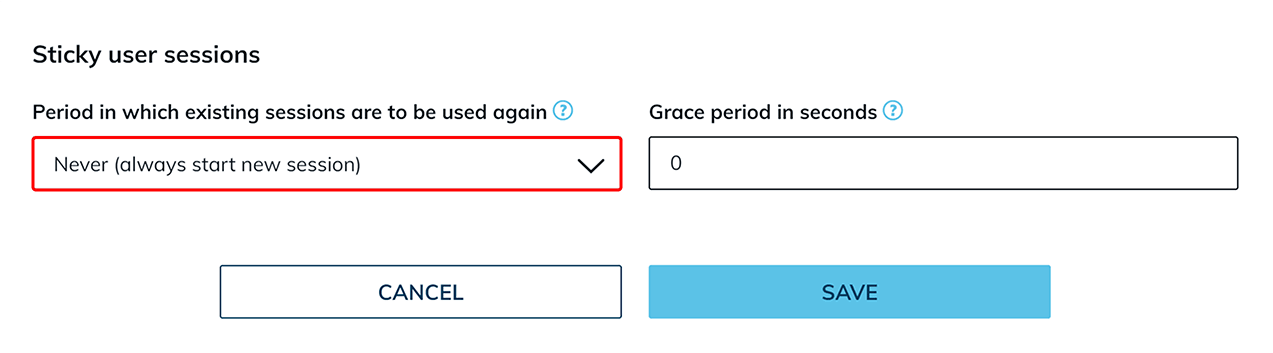 In addition, you have the option to set a grace period. This is necessary, for example, for restoring roaming profiles if they are in use. To do so, enter the amount of time that you think is sufficient for this process in the corresponding field under the item “Grace period in seconds”.
In addition, you have the option to set a grace period. This is necessary, for example, for restoring roaming profiles if they are in use. To do so, enter the amount of time that you think is sufficient for this process in the corresponding field under the item “Grace period in seconds”.
The recommended length of the grace period depends on many factors and should be determined individually and adjusted after an appropriate test phase. A longer grace period is recommended especially for operations with a high volume of data, such as editing large files. If the “Never” option is selected, the grace period is always “0”. Although it is possible to enter another time period in the corresponding field, such an entry will not be valid.
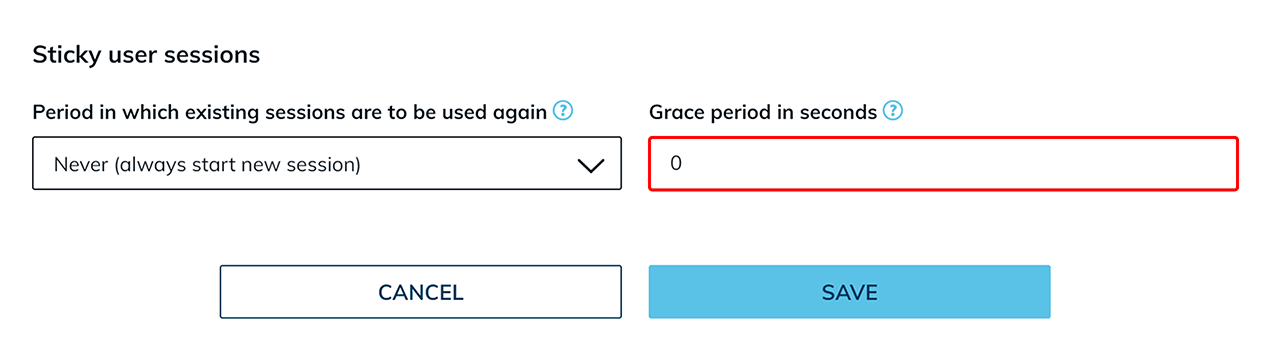
A maximum period of two hours can be selected here. Note, that as the length of this period increases, the effect of load balancing decreases more and more. We recoomend setting the value here as low as possible.
Finally, confirm your entries with Save.
Configure Sticky Sessions in Windows (optional)
To ensure that the same value is also set in all of your connected Windows resources, you should also set this configuration in the operating system of the respective resource. To do so, follow our instructions for setting the time limit for disconnected sessions.